Cardiac
Table of contents
Anatomy
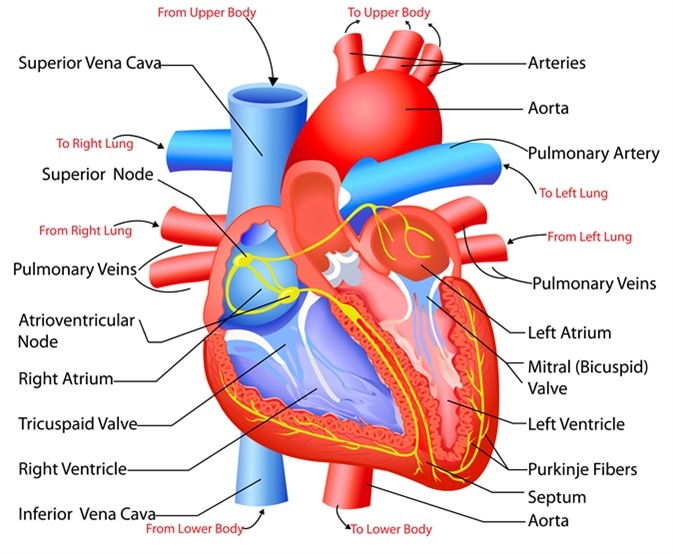
- Right side: de-oxygenated blood
- Left side: oxygenated blood
Remember pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood from lungs to heart
Layers of heart
Inside out
- Endocardium
- Myocardium
- Epicardium / pericardium
Coronary blood supply
Coronary arteries
- Sit epicardially, extend into the myocardium via smaller branches
- Receive their oxygenated blood supply during the diastole phase of the cycle
- This becomes more important in tachycardias where diastole is reduced
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
Right atrium, right ventricle, SA and AV notes
Posterior descending artery (PDA)
Right ventricle, posterior left ventricle
Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
Left ventricle including some septum, possibly some of the right ventricle
Left circumflex (LCx)
Lateral left ventricle, left atrium
Left anterior descending (LAD)
Septum, anterior left ventricle, apex of the left ventricle
Auto-regulation
Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic
Dilated
Restrictive
Cardiomegaly
Useful formula
Cardiac Output
5-6L/min normal range
Factors that affect Cardiac Output (CO)
Stroke Volume
- Heart size
- Fitness level
- Gender
- Contractility (autonomic innervation and hormones)
- Duration of contraction
- Preload (End diastolic volume - venous return, filling time)
- Afterload (Resistance - so think about vasodilation/vasoconstriction)
Heart Rate
- Autonomic innervation
- Hormones
- Fitness level
- Age
Stroke Volume
40-90ml/beat normal range
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
80-120mmHg normal range